In this post, we will be discussing that how independent sample t-test is conducted on SPSS. This test is used when we want to test the hypothesis regarding the means belonging to two separate groups. Lets illustrate this with an example.
Suppose that you are an HR Manager for a large organization and want to find out that if there is some wage differences between male and female salaries. To test this, you can follow the process by developing hypothesis, collecting data, running the independent sample t-test, accepting or rejecting the hypothesis, and then arriving on conclusion.
First you will develop the hypothesis, a sample is as under.
H0 (Null Hypothesis) = There is no differences between the male and female wages in this organization
H1 (Alternative Hypothesis) = There is significant differences between the male and female wages in this organization.Male= 1500, 2500. 3500, 1000, 2500, 1500, 2000, 2000, 2500, 3000 Female= 1000, 1000, 1500, 1000, 2000, 2500, 1500, 1000, 1500, 2000
H0 (Null Hypothesis) = There is no differences between the male and female wages in this organization
H1 (Alternative Hypothesis) = There is significant differences between the male and female wages in this organization.Male= 1500, 2500. 3500, 1000, 2500, 1500, 2000, 2000, 2500, 3000 Female= 1000, 1000, 1500, 1000, 2000, 2500, 1500, 1000, 1500, 2000
To test the hypothesis, suppose you collect data from 30 respondents where 15 were male and 15 were female. The data for both groups is as under in US dollars weekly salary.
Now if you calculate simply the average for both groups, you will get average salary of male as US$ 2200, while average salary for female is US$ 1500. However, to test that whether these differences are really significant , you need to run the independent sample t-test.
First input the two variables namely Gender and Wages in US$ and relevant data in SPSS. (For details on how to input the variable and data in to SPSS, Please see my previous posts).
Once you have setup the variables and data, then you are in position to actually run the test.
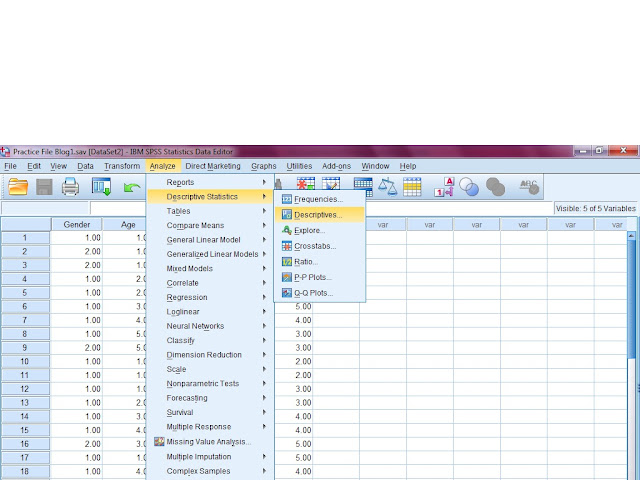
Analyze---Compare Means--- Independent Sample t-test
A dialogue box will appear, where, you will be able to see the both variables.
First, transfer the Wages variable in to Test Variable box. Then, transfer the Gender variable in to Grouping Variable box and then click on Define Groups. Another dialogue box will appear where simply write 1 and 2 in group 1 and 2 accordingly. Now click on Continue and then on OK. The results will appear in output window which can be interpreted as under.
The first table with the heading ‘Group Statistics’ is simply giving basic information on the mean of both groups. In this example, the average wages for both male and female are shown in this table which shows that for male the average salary is US$ 2200 and for female the average salary is US$ 1500. In next column, there is standard deviation given which is used to judge the measure of dispersion or the variation in the data from its mean point.
In the second table with the heading ‘Independent Samples Test’ there is various statistics given. The value of t and Sig (2-tailed) is used to test the hypothesis. In this example, the value of t is 2.409 which is greater than the standard test value of 2. Similarly, the value of sig is also less than 0.05; therefore, we can reject the null hypothesis and accept the alternative hypothesis. (Hypothesis is normally accepted when Sig value is less than 0.05. It is also called P value)Thus conclusion is that there is significant differences exist between the average salary of male and female in this organization.
Sample Practice File is as under.
For details on Online Classes for SPSS contact the following:
Email: onlinetrainingsolution@gmail.com
Skype Id: faireast1
Mobile: +92-3239256994
Facebook Page: Online Training Solution
Facebook Page Link
Skype Id: faireast1
Mobile: +92-3239256994
Facebook Page: Online Training Solution
Facebook Page Link
Thank You